What Are Antibodies Describe How They Are Formed
Antibodies are part of the human immune system. This process is called agglutination.

Structure And Function Of Antibody Britannica
Antibodies are typically made of the same basic structural units each with two.
. When an antigen binds to the B-cell surface it stimulates the B cell to divide and mature into a group of identical cells called a clone. Antibodies defend us against infection by binding to viruses and microbial toxins thereby inactivating them see Figure 24-2. Click card to see definition.
IgG is the most abundant antibody isotype in the blood plasma accounting for 70-75 of human immunoglobulins antibodies. The B cells produce antibodies that are used to attack invading bacteria viruses and toxins. And they trigger destruction of pathogens by stimulating other immune responses such as the complement pathway.
They prevent pathogens from entering or damaging cells by binding to them. Antibodies are heavy 150 kDa globular plasma proteins. These antibodies can then be collected directly in the serum or by isolating the individual B cells that.
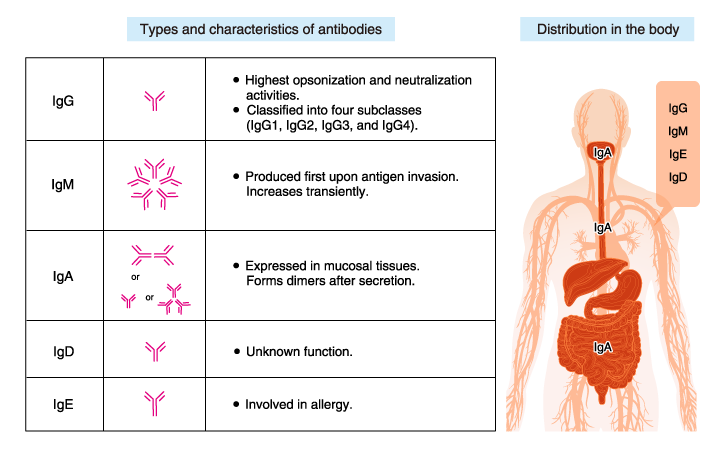
Tap card to see definition. Antibodies trigger your immune system to fight infection. Human antibodies are classified into five isotypes IgM IgD IgG IgA and IgE according to their H chains which provide each isotype with distinct characteristics and roles.
These antibodies remain in the blood. The white blood cells and activated complement components work. IgG detoxifies harmful substances and.
Now there are different types of antigens but for our purposes here lets zoom in on foreign disease-causing antigens. However the choice of an adequate production system depends on the antibodys intended application. Antibodies are produced by a type of white blood cell called a B cell B lymphocyte.
They stimulate removal of pathogens by macrophages and other cells by coating the pathogen. B cells and T cells. Pathogens have proteins on their surface called antigens.
They process pathogens viruses bacteria etc that have entered the body and dead cells by preying upon and digesting them. IgM antibodies are the first antibodies the body produces. A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell that is part of the immune system.
Natural antibodies are the first line of the organisms defence before the. Antibodies contribute to immunity in three ways. Because the arms of the Y-shaped antibodies attach randomly to more than one nonself erythrocyte surface they form clumps of erythrocytes.
Some antigens destroy pathogens while others bind to the pathogen and send out signals to alert the immune system to invaders that need to be attacked. The clumps of erythrocytes block small blood vessels throughout the body depriving tissues of oxygen and nutrientsAs the erythrocyte clumps are degraded in a process called hemolysis. When an intruder enters the body the immune.
Antibodies are produced by specialized white blood cells called B lymphocytes or B cells. And antigens are substances that can stimulate the bodys production of antibodies. There are two main types of lymphocytes.
Plasma cells create antibodies specific to a certain antigen. B cells develop from stem cells in bone marrow. In contrast to adaptive antibodies natural antibodies are present in a non-immunised organism from birth and they do not include anti-Gal antibodies andor anti-Gal natural antibodies which are developed as a result of the effect of the α-Gal epitope and physiological flora.
Antibodies are Y-shaped proteins that bind to the bodys foreign invaders and signal the immune system to get to work. These immunoglobulins undergo mitosis resulting in cell division and continuously produce antibodies as a result of producing more cells. Read the complete article to find out how to choose the best production system for each.
Monoclonal antibodies can be produced in a variety of recombinant systems including mammalian microbial bacterial and yeast or insect cells. These are critical for preventing future infection. Later your body makes IgG antibodies.
2 Antibodies activate the complement system to destroy bacterial cells by lysis punching holes in the cell wall. 1 Antibodies are secreted into the blood and mucosa where they bind to and inactivate foreign substances such as pathogens and toxins neutralization. Antibodies are not found at a place as such but whenever our immune system encounters antigen or a pathogen B cells get activated immediately releasing antibodies into the bloodstream.
-Specific antigen injected into animal eg. Furthermore they serve a role of notifying other cells of the antigens on the surface of the pathogens being preyed upon antigen-presenting capacity. They connect to a specific spot on a virus to inactivate it.
When B cells become activated due to the presence of a particular antigen they develop into plasma cells. In other words they are glycoproteins. Antibodies also known as immunoglobulins are Y-shaped proteins that are produced by the immune system to help stop intruders from harming the body.
Basically they identify bad bacteria and viruses and track them down to fight back. The binding of antibodies to invading pathogens also recruits various types of white blood cells and a system of blood proteins collectively called complement discussed in Chapter 25. They have sugar chains added to some of their amino acid residues.
Antibodies are special protein molecules that the immune system produces in response to antigens. Describe how monoclonal antibodies are produced. -B-lymphocytes fuse with myeloma cells to form hybridoma cells - these cells can divide and produce antibodies.
-B-lymphocytes producing complementary antibodies extracted. The mature B cells called plasma cells secrete millions of antibodies into the bloodstream and lymphatic system. Antibodies are proteins produced by a type of white blood called lymphocytes.
Antibodies are proteins made by the immune system that mount a defense against viruses bacteria and other pathogens that can make you sick. From the perspective of developing a custom antibody against a protein antigen the immune system captures the protein breaks it down into individual epitopes and presents these epitopes to the B cells so that development of antibodies specific to those epitopes can begin. The T cells destroy the bodys own cells that have themselves been taken over by viruses or become cancerous.

How Are Antibodies Produced Sino Biological

0 Response to "What Are Antibodies Describe How They Are Formed"
Post a Comment